Firishta was born at Astrabad on the shores of the Caspian Sea to Gholam Ali Hindu Shah. While Firishta was still a child, his father was summoned away from his native country into Ahmednagar, India, to teach Persian to the young prince Miran Husain Nizam Shah, with whom Firishta studied.
In 1587 Firishta was serving as the captain of guards of King Murtuza Nizam Shah when Prince Miran overthrew his father and claimed the throne of Ahmednagar. Prince Miran spared the life of his former friend, who then left for Bijapur to enter the service of King Ibrahim Adil II in 1589.
Having been in military positions until then, Firishta was not immediately successful in Bijapur. Further exacerbating matters was the fact that Firishta was of Shia origin and therefore did not have much chance of attaining a high position in the dominantly Sunni courts of the Deccan sultanates. In 1593 Ibrahim Shah II ultimately implored Firishta to write a history of India with equal emphasis on the history of Deccan dynasties as no work thus far had given equal treatment to all regions of the subcontinent.
According to the scholar T. N. Devare, Firishta's account is the most widely quoted history of the Adil Shahi, but it is the only source for a fabricated story asserting the Ottoman origin of Yusuf Adil Shah, the founder of the Adil Shahi dynasty (Devare 67 fn2, 272). Other sources for Deccani history mentioned by Devare are those of Mir Rafi-uddin Ibrahim-i Shirazi, or "Rafi'", Mir Ibrahim Lari-e Asadkhani, and Ibrahim Zubayri, the author of the Basatin as-Salatin (67, fn 2). Devare observed that the work is "a general history of India from the earliest period up to Firishta's time written at the behest of Ibrahim Adilshah II and presented to him in 1015 AH/1606 CE. It seems, however, that it was supplemented by the author himself as it records events up to AH 1033 (1626 CE)" (Devare 272).[citation needed]
On the other hand, Tarikh-i-Farishti is said to be independent and reliable on the topic of north Indian politics of the period, ostensibly that of Emperor Jehangir where Firishta's accounts are held credible because of his affiliation with the south Indian kingdom of Bijapur.
Despite his fabricated story of Yusuf's Ottoman origin, Firishta's account continues to be a very popular story and has found wide acceptance in Bijapur today.
In 1768, when the East India Company officer and Orientalist Alexander Dow translated Firishta's text into English language, it came to be seen as an authoritative source of historical information by the English.
Firishta's work still maintains a high place and is considered reliable in many respects. Several portions of it have been translated into English; but the best as well as the most complete translation is that published by General J. Briggs under the title of The History of the Rise of the Mahomedan Power in India (London, 1829, 4 vols. 8vo). Several additions were made by Briggs to the original work of Firishta, but he omitted the whole of the twelfth book, and various other passages which had been omitted in the copy from which he translated. Edward Gibbon used Firishta's work as one of the sources of reference for Indian history in Decline and Fall.
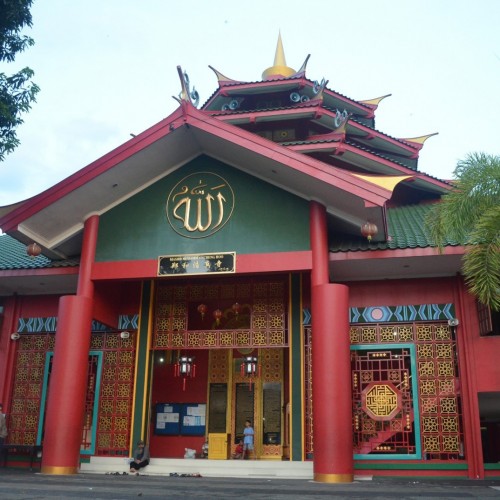

 Muhammad Cheng Ho Mosque, Pandaan, Pasuruan, East Java, Indonesia
Muhammad Cheng Ho Mosque, Pandaan, Pasuruan, East Java, Indonesia