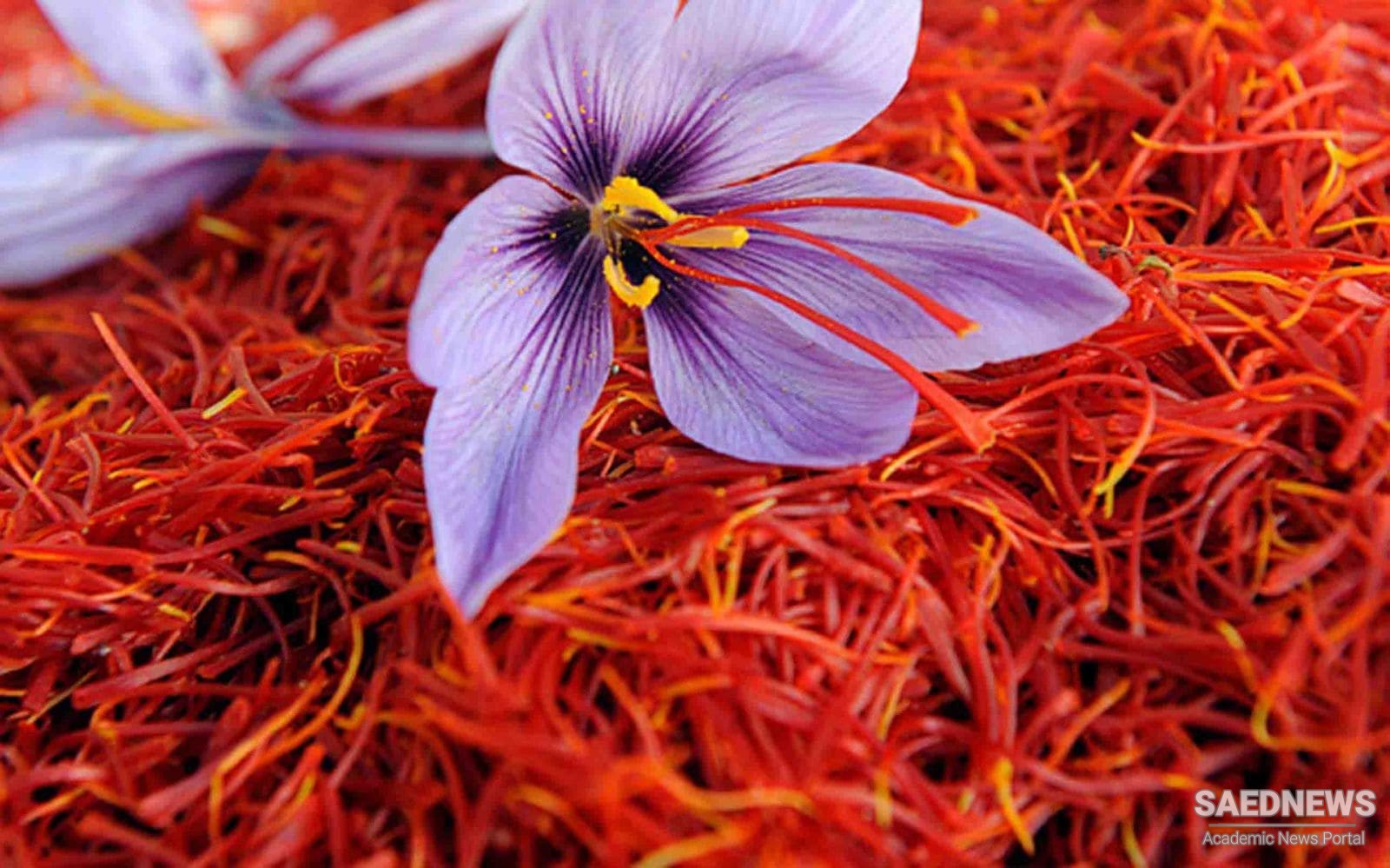
Saffron is a perennial plant that grows up to 30 cm in height. This plant has six-petal purple flowers with three stamens and a pistil leading to the three-branched red stigma. The part used in this plant is the end of the plant's style and the three-branched stigma, which is known as saffron and has a fragrant smell. Known as red gold, this valuable plant is the main source of income in most regions of Khorasan province of Iran.
Saffron contains an impressive variety of plant compounds that act as antioxidants — molecules that protect your cells against free radicals and oxidative stress.
Notable saffron antioxidants include crocin, crocetin, safranal, and kaempferol.
Crocin and crocetin are carotenoid pigments and responsible for saffron’s red color. Both compounds may have antidepressant properties, protect brain cells against progressive damage, improve inflammation, reduce appetite, and aid weight loss.
Safranal gives saffron its distinct taste and aroma. Research shows that it may help improve your mood, memory, and learning ability, as well as protect your brain cells against oxidative stress.
Lastly, kaempferol is found in saffron flower petals. This compound has been linked to health benefits, such as reduced inflammation, anticancer properties, and antidepressant activity.

 Iranian Cuisine
Iranian Cuisine