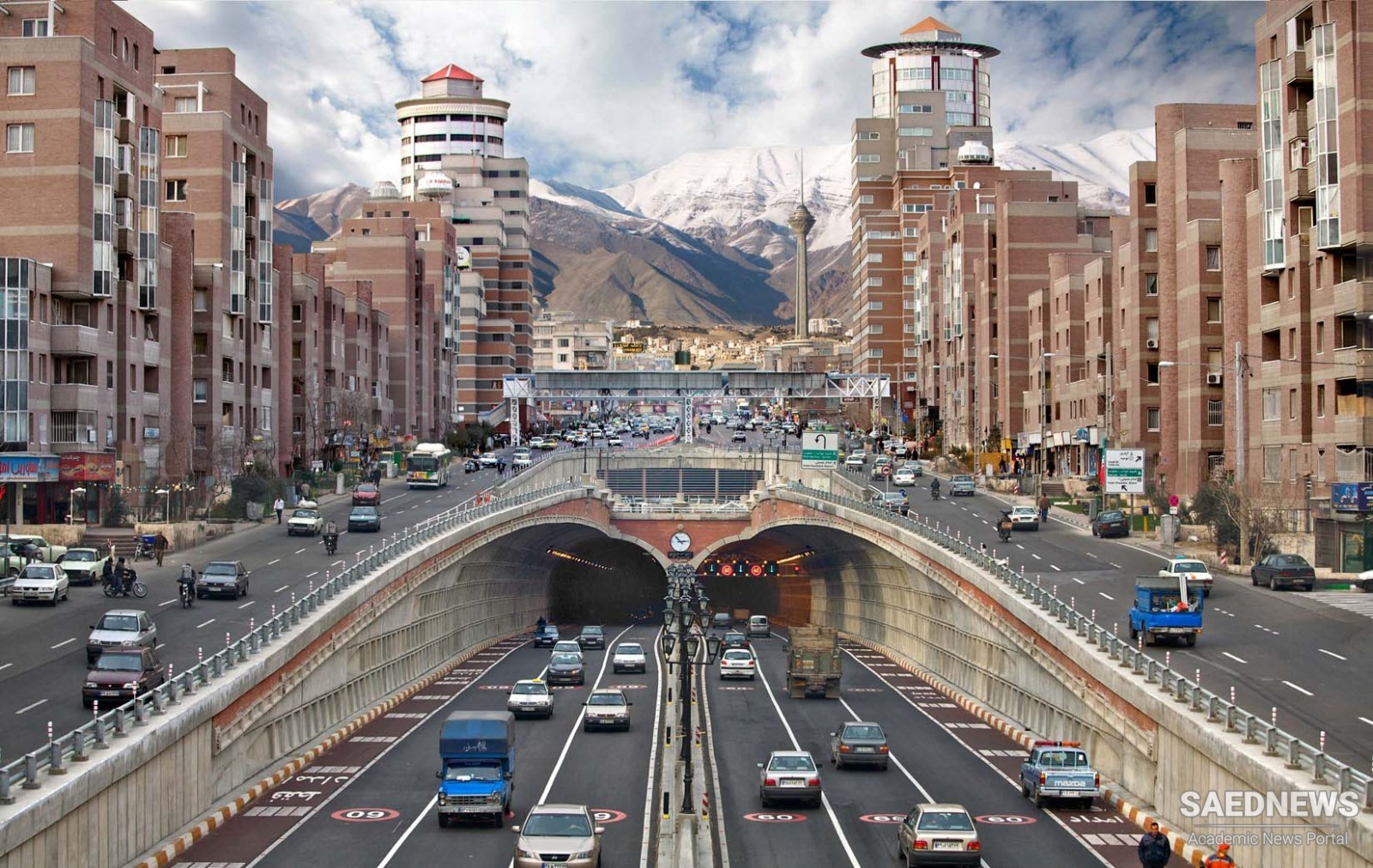
Tehran is the capital of Iran, The population of the city is almost 14 million with a metropolitan area population of approximately 17 million.
Human settlement of the region dates from Neolithic times, but the development of Tehran was very slow and its rise to prominence largely accidental. From the mid-16th century, Tehran’s attractive natural setting and good hunting brought it into the favor of the Safavid kings. It developed from a moderately prosperous trading village into an elegant, if dusty, city, and European visitors wrote of its many enchanting vineyards and gardens. In 1789, Agha Muhammad Khan declared Tehran his capital, and six years later had himself crowned as Shah of all Persia. The town continued to grow slowly under later Qajar rulers.
From the early 1920s, the city was extensively modernized on a grid system, and this period marked the start of phenomenal population growth and uncontrolled urban development that continues to this day. Today Tehran is so vast that getting hopelessly lost at least once in a year is certain, no matter what form of transport you take. If you need landmarks, the Alborz mountains, known as the ‘North Star’ of Tehran, are to the north; and the huge telephone office at Emam Khomeini Square dominates inner southern Tehran.
Tehran is a cosmopolitan city, with great museums, parks, restaurants, and warm friendly people. It deserves at least a few days of your Iranian itinerary.
The city can be roughly divided into two different parts – north and south. The northern districts of Tehran are more prosperous, modern, cosmopolitan and expensive while southern parts are less attractive but cheaper.
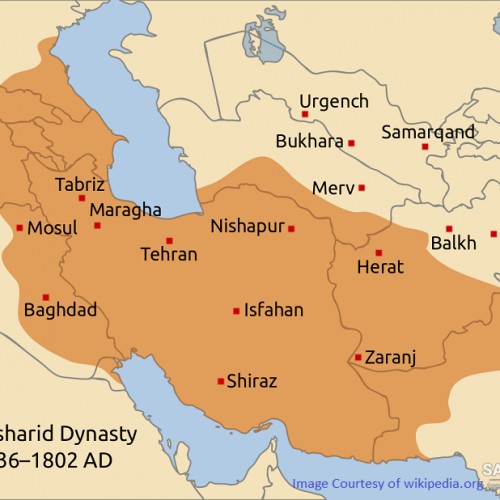
At the time of the Zand dynasty, it was a little town that was significant from a strategic point of view. The first of the Qajar kings, Agha Mohammed Khan, named Tehran as the country’s capital in 1778, and most of its growth started during the reign of a subsequent Qajar monarch, Fath-Ali Shah. The castle which Agha Mohammed Khan had built was to contain the new majestic buildings.


 Abbas Qoli Khan Shamlu’s Seminary of Religious Sciences in Mashhad
Abbas Qoli Khan Shamlu’s Seminary of Religious Sciences in Mashhad