A growing number of destinations are promoting their cuisine as a core tourism product. This is particularly relevant to destinations with well-known cuisines as well as wine-producing regions, where fine wine and fine food frequently go hand-in-hand. Yet, it is important that food tourism is sustainable and retains a destination’s cultural identity. Those pursuing a career in hospitality must develop the skills and knowledge to balance the benefits of food tourism while limiting its potential negative drawbacks.
- Benefits of food tourism: According to the WFTA, food tourists spend about 25% of their travel budget on food and beverages. This can mean an increase in profits for a local community as well as the local government’s budget due to the taxes imposed on the goods purchased by tourists. This rise in revenue can afford local governments the ability to invest in marketing to tourists, which in turn can boost profits for local shops, restaurants, hotels and transportation services. An increase in culinary tourism can also instill in locals cultural pride and help ensure unemployment rates remain low, especially in rural areas with low economic activity.
- Drawbacks of food tourism: Though food tourism can have many desirable effects on a local community, in some cases the negatives may outweigh the positives. For communities that are suffering from a lack of natural resources — food, water, electricity — tourism can negatively affect the lives of those in the community. Fresh water may be re-routed to crops to sustain tourists’ demand for food, while the locals’ ability to have fresh water and food can be diminished.
Some communities can face loss of cultural identity, because the local economy has transitioned to supporting the needs of tourists. Restaurants may begin to refrain from serving local cuisine and change menus to suit the culinary needs of tourists. In some cases, the influx of tourists can drive up the prices of goods and services, which forces many locals out of their communities, thus destroying a community’s unique character.
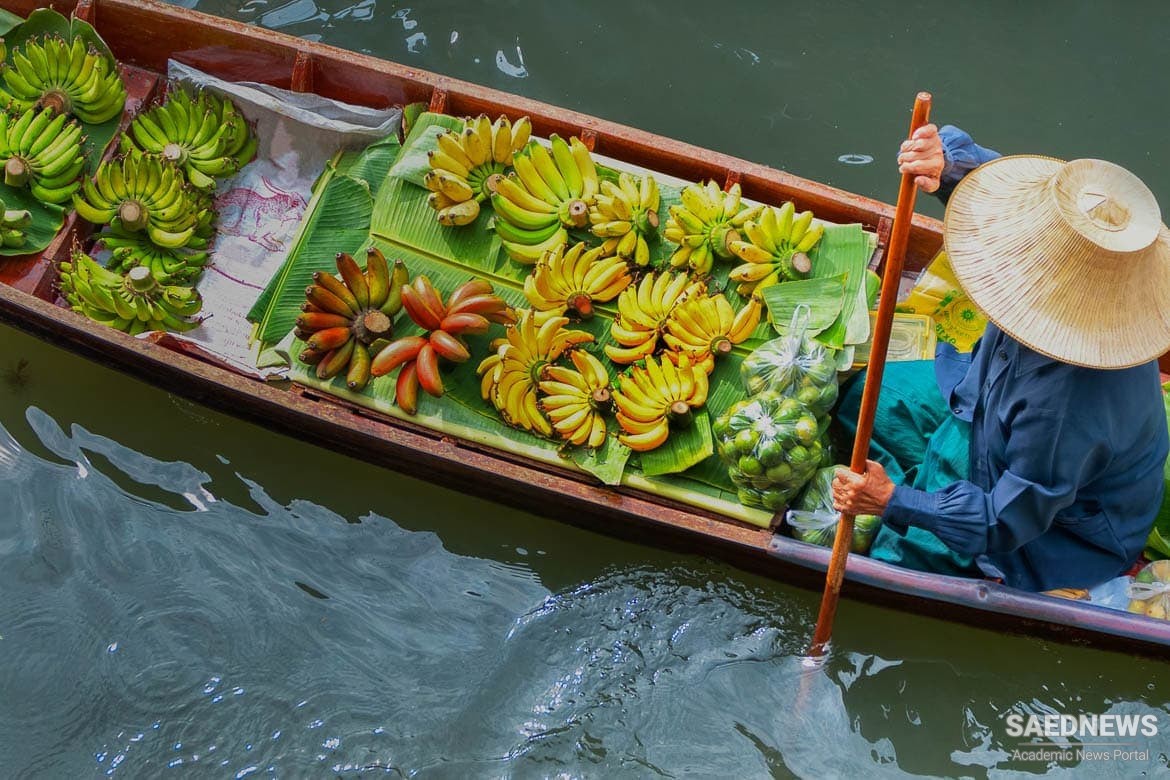
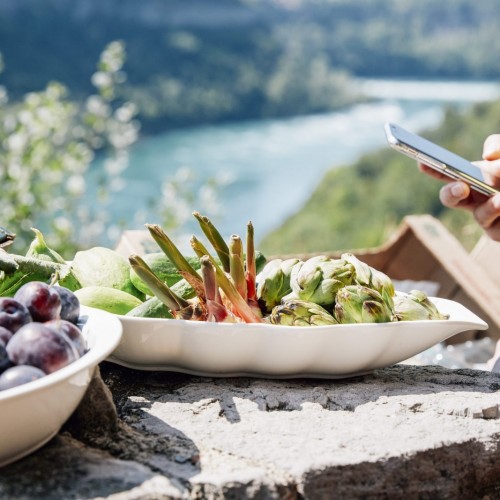

 Levels and Types of Tourist Interest in Food Tourism
Levels and Types of Tourist Interest in Food Tourism