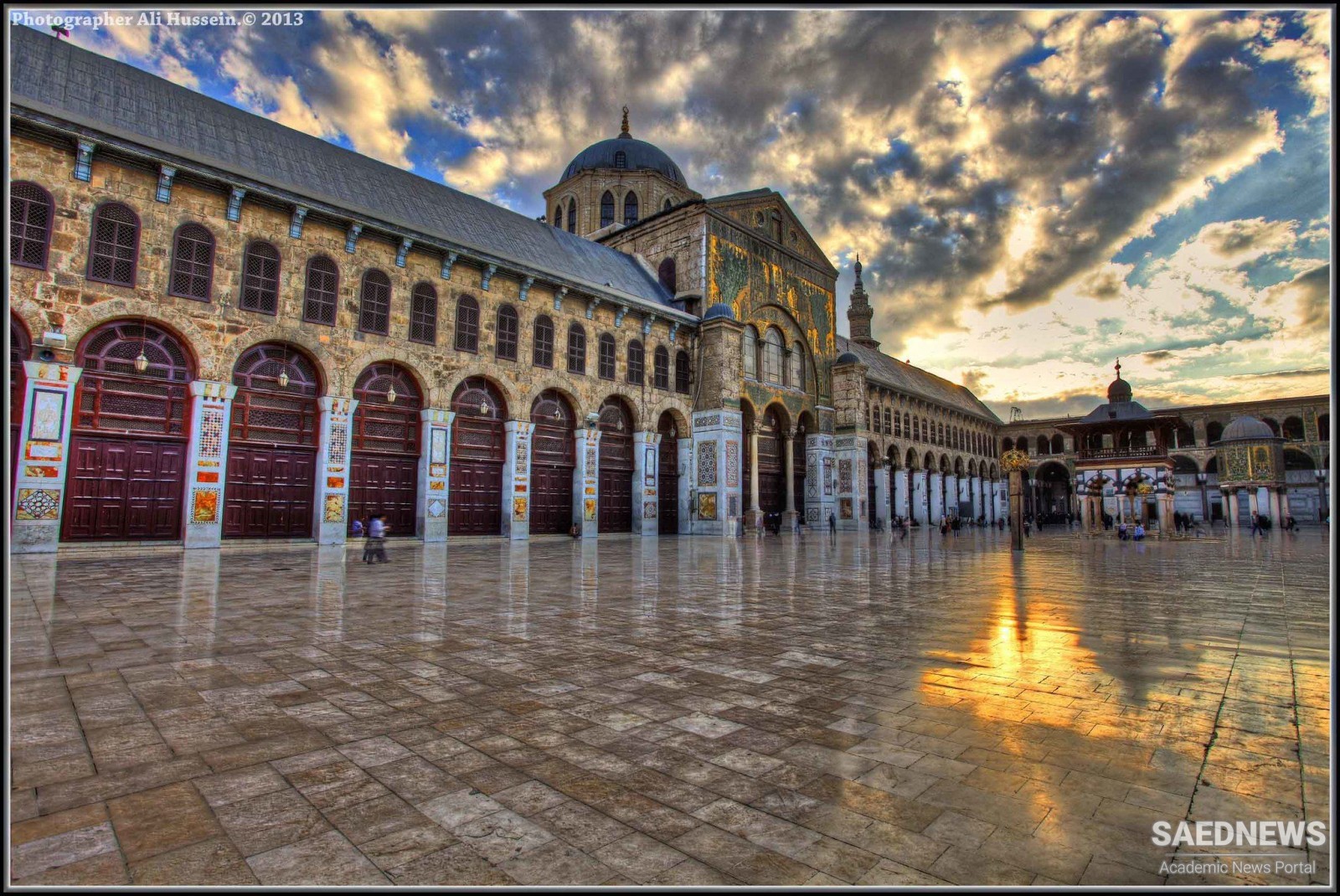
The Umayyad Mosque (or Masjid), also known as the Grand Mosque of Damascus is one of the largest and oldest mosques in the world. It is the first monumental work of architecture in Islamic history. The spot where the mosque now stands was originally a temple dedicated to the idol Hadad in the Aramaean era about 3000 years ago. When the Romans ruled Damascus a temple was built for the worship of Jupiter. It then became a Christian church dedicated to John the Baptist in the Byzantine era towards the end of the fourth century. Following the Battle of Yarmouk in 636 CE, Damascus was conquered by the Muslims under the leadership of Khalid-bin-Waleed. The Muslims shared the church building with the Christians for worship. The Muslims prayed in the eastern section of the structure and the Christians in the western side. This collective use continued until the reign of the Umayyad caliph al-Walid I, when the prayer space became inadequate both in terms of capacity and the need for an architectural monument to represent the new religion. The caliph negotiated with Christian leaders to take over the space, and in return al-Walid promised that all the other churches around the city would be safe, with the addition of a new church dedicated to the Virgin granted to the Christians as compensation. The church was purchased from the Christians before being demolished and between 706 and 715 CE the current mosque was built in its place. Construction of the mosque was based on the mosque of the Prophet Muhammad in Madinah, which had many functions: it was a place for personal and collective prayer, religious education, political meetings, administration of justice, and relief of the ill and homeless. The caliph asked and obtained from the Emperor of the Byzantine Empire for 200 skilled workers to decorate the mosque, as evidenced by the partly Byzantine style of the building. The new mosque was the most impressive in the Islamic world at the time, and the interior walls were covered with fine mosaics. The building became one of the marvels of the world, because it was one of the largest of its time. The exterior walls were based on the walls of the temple of Jupiter and measure 100 by 157.5 m (Source: Islamic Landmarks).








 Ummayyads in Persia: Abdul Malik I and His Economic Initiatives
Ummayyads in Persia: Abdul Malik I and His Economic Initiatives